INDUCTION
x
1. INDUCTION
Induction (from Latin inductio) is the interaction of tissues, in which one tissue (the inductor or organizer) directs the development of another adjacent tissue to differentiate in a way it otherwise would not (i.e. it generates new cell types). Induction occurs only for a limited time during early development. As differentiation of cells proceeds, tissues lose their ability of induction or their ability to respond to inductive signals.
| Inductor must be close to but not necessarily in contact with the tissue to be induced. Example: Motoneurons have been induced by a diffusible factor from the notochord or the floor plate, whereas dopaminergic neurons require cell - cell contact with floor plate cells. |
|
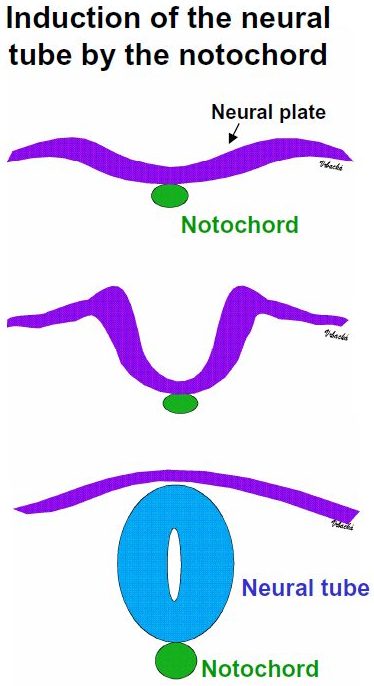 |
Fig. Induction of the neural tube by the notochord. The developing notochord (axial mesodermal tissue – in green) induces the overlying ectoderm (purple) to proliferate to form the neural plate. Due to cell proliferation the neural plate is converted to a longitudinal neural groove; its neuroectoderm is linked to the superficial ectoderm via neural folds. Detachement of neuroectoderm from ectoderm (see "Apoptosis") allows a close contact of both folds and formation of the neural tube (blue) while dorsal surface is covered by the ectoderm. |
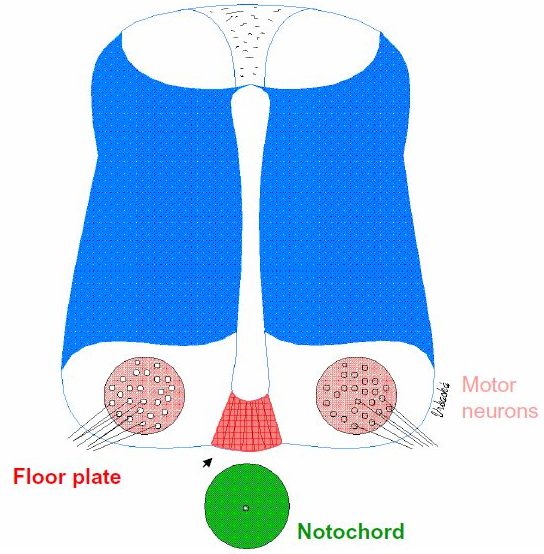
Fig. Regionalization of the neural tube with the inductor.
 |
 |
 |
| Fig. 1 | Fig. 2 | Fig. 3 |
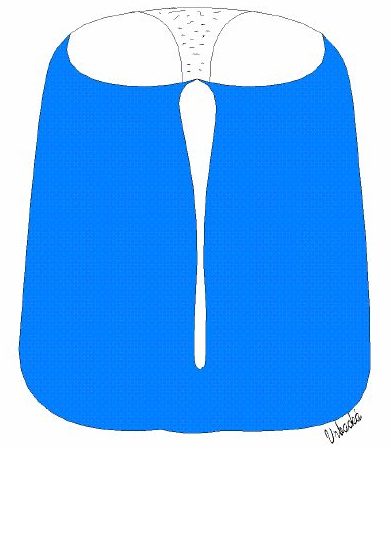
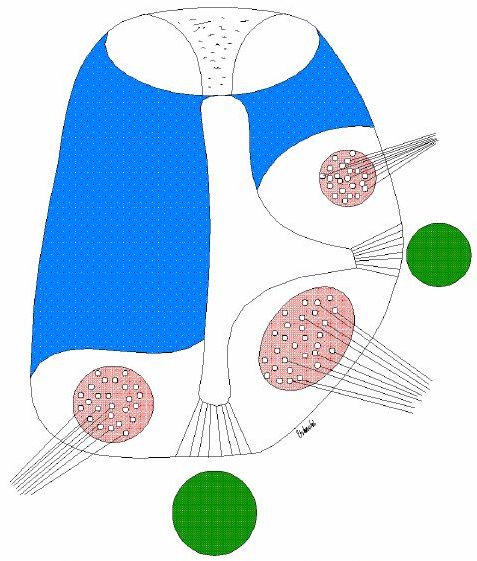
| Fig. 1. The notochord and the ventral floor are responsible for regionalization of the neural tube in the transverse plane. The notochord and the floor plate induce neural precursor cells of the neural tube to assume fates of ventral neurons (eg. motor neurons of the spinal cord, serotonergic neurons of the hindbrain or dopaminergic neurons of the ventral mesencephalon – these cells receive the highest concentration of signalling molecules) - secondary induction. Distant cells in a ventral part of the neural tube that obtain a lower concentration of signals diffusing from the notochord are changed into dorsal neuron type, i.e. interneurons. Fig. 2. In the absence of any outside inductor, the cells of the neural tube spontaneously express a dorsal fate, i.e. no floor plate or motoneurons differentiate. Fig. 3. An ectopic notochord (green) placed lateral to the neural tube triggers induction of an extra floor plate and extra motoneurons. Author of figures: Jaroslav Mokrý |
||
